Section: New Results
Hierarchical Region-Network Sparsity for High-Dimensional Inference in Brain Imaging
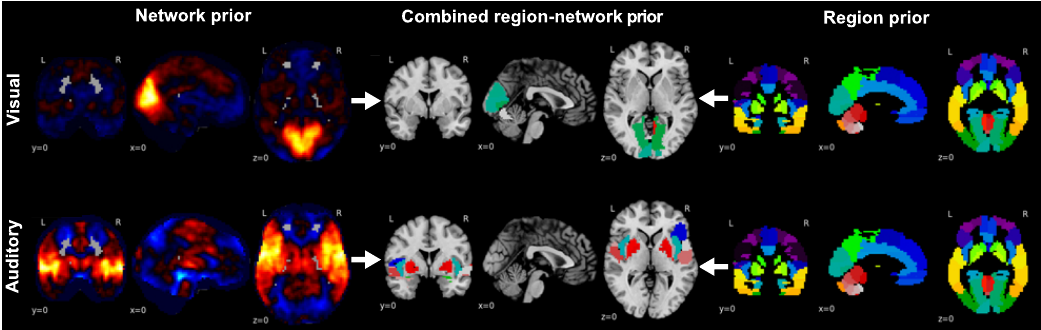
Structured sparsity penalization has recently improved statistical models applied to high-dimensional data in various domains. As an extension to medical imaging, the present work incorporates priors on network hierarchies of brain regions into logistic-regression to distinguish neural activity effects. These priors bridge two separately studied levels of brain architecture: functional segregation into regions and functional integration by networks. Hierarchical region-network priors are shown to better classify and recover 18 psychological tasks than other sparse estimators. Varying the relative importance of region and network structure within the hierarchical tree penalty captured complementary aspects of the neural activity patterns. Local and global priors of neurobiological knowledge are thus demonstrated to offer advantages in generalization performance, sample complexity, and domain interpretability.
More information can be found in Fig. 7 in [48].
|